Most records of training for compliance training are valid for three years. A lot can happen in terms of regulatory requirements in three years. This article, summarizes information from two articles which first appeared in the Sep/Oct and Nov/Dec 2014 editions of Propane Canada Magazine. This article discusses the importance of ensuring you are keeping regulatory training current so that your employees remain properly trained.
As detailed in previous articles earlier this year the B149.1 – Natural Gas and Propane Installation Code and the B149.2 – Propane Storage and Handling Code have been extensively amended for publication by the Canadian Standards Association in 2015.
Also, the B149.3 – Code for the Field Approval of Fuel Related Components on Appliances and Equipment and the B149.5 – Installation Code for Propane Fuel Systems and Tanks on Highway Vehicles will have new Codes published by the Canadian Standards Association in 2015.
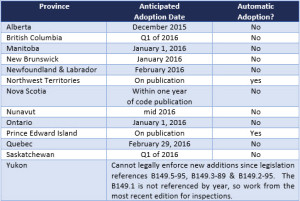
The provincial adoption of the 2015 codes will start to take place sometime after January 2015. Some provinces adopt the codes as soon as they are published, while other provinces adopt several months later. It is, therefore, important that, as users of the Codes, you are aware of when your particular province will adopt the Codes that regulate the work you perform.
Ontario Adoption of Codes
 Ontario has issued an Ontario Code Adoption Document (CAD) for both 2010 editions of B149.1 and B149.2 codes which become effective October 1, 2014. The CAD adopts many of the changes that will appear in the 2015 editions of the B149.1 and B149.2 codes. The CADs are available on the TSSA website for download. Significant changes made by the Gaseous Fuels amendment include:
Ontario has issued an Ontario Code Adoption Document (CAD) for both 2010 editions of B149.1 and B149.2 codes which become effective October 1, 2014. The CAD adopts many of the changes that will appear in the 2015 editions of the B149.1 and B149.2 codes. The CADs are available on the TSSA website for download. Significant changes made by the Gaseous Fuels amendment include:
- Permitting press-connect fittings;
- Re-classifying clothes dryers in accordance with the certification standard;
- Adding a new section regulating unvented heaters installed in livestock or poultry facilities;
- Incorporating Director’s Order FS-051-04 (re B-Vents not certified for exterior applications installed outdoors) into the code, for ease of reference; and
- Adoption of TSSA-MFSE-2014 for field approval of mobile food service equipment.
The Propane Storage & Handling Code Adoption Document adopts the 2010 edition of the Code and new requirements approved by the B149.2 and B149.5 Code Committees for the 2015 Code which are considered important to be implemented in Ontario now and addresses gaps in the current codes to enhance safety.
Major changes in this version include the following:
- New definitions added for “construction site” and “cylinder exchange”;
- New requirements for cylinder storage, including storage at construction sites and rooftops;
- New requirements for cylinder exchanges;
- Reiterating the need for compliance with Branch Standard #9 or a full risk and safety management plan for facilities in heavily populated or congested areas; and
- New certification requirements for valves, components, and accessories for propane vehicle conversion; replacing IGAC Protocol 01-97.
Code Updates Referred to in TDG Regulations
At the same time there is a new, 2014 edition of the B620 – Highway Tanks and Portable Tanks for the Transportation of Dangerous Goods and B622 – Selection and Use of Highway Tanks, Multiunit Tank Car Tanks, and Portable Tanks for the Transportation of Dangerous Goods, Class 2.
While Transport Canada recently adopted the 2009 editions of the CSA/B620 and CSA/B622, the 2014 editions are completed and ready for adoption. It is important for one to keep abreast of the latest Codes and Standards as you know eventually any new requirements will become law.
Training Requires Updating
Once the Codes and Standards are adopted there will be an immediate training need for persons who perform work that is regulated by these documents. In Ontario, this is October 1, 2014, which means that training programs that are used by the propane industry to train people must reflect the latest regulatory requirements as of October 1, 2014, for Ontario and in other provinces early next year.
This does create some issues as the current Record of Training (ROT) retraining requirements are once every 3 years, which means that people can actually be working in the field for up to 3 years before they are trained on the new regulatory requirements.

Given that 2015 is the year for the issuance of new codes it may be advisable for employers in certain segments of the industry such as gas technicians, propane cylinder, cargo liner and bulk delivery and propane construction heating, to have their employees trained on the new requirements rather than wait until such time that the person’s ROT is up for renewal.
One of the largest impacts is going to be in the construction industry where the requirements for the storage and use of cylinders have been extensively amended. If your cylinder delivery driver is not aware of the new requirements he could inadvertently create a non-compliance situation which could result in fines and disruption of service to your customer.
For example, Ontario Director’s Order FS-095-06, issued November 2013, states that “when distributors provide fuel to tanks or cylinders not connected to the premises, the distributor shall ensure that the fuel storage is compliant with Ontario Regulation 211/01”.
If not aware of the new requirements, the contractor who uses the propane cylinders and construction heaters can also inadvertently create a non-compliant situation which could result in fines and impact the ongoing construction of the building. The contractor could also be at a disadvantage from an efficiency perspective if he does not know the new requirements with respect to the use and storage of propane cylinders on rooftops.
Another example is the increased size of cylinders which may be stored in cylinder exchange cabinets. Due to demand from the RV industry, the maximum was changed from 20 lb. 30 lb. cylinder sizes. The cabinet maximum capacity of 500 lb. (25 x 20 lb., or 16 x 30 lb., or a combination thereof) has been maintained. If you were not aware of these new requirements you could be missing out on an opportunity to serve the recreational market with the larger propane cylinders.
The CSA-B620-14 has new requirements for “off truck emergency shutdown system” to include tanks in non-metered propane delivery as well as engine shutdown when the engine air intake senses flammable vapors. When adopted, drivers of unmetered deliveries need to be trained in the inspection and use of these new requirements
It does not make economical or practical sense to train people with outdated training programs. As indicated by the examples above it is crucial to one’s business that employees are trained in understanding the latest regulatory requirements.
Status of publication of the 2015 series of CSA Codes and Standards
2015 B149.1 – Natural Gas & Propane Installation Code
The committee last met on June 12, 2014. Public Review took place from March 12 to May 12, 2014; and all comments were dispositioned and resolved. There was a general consensus on the draft and it proceeded to the editing stage. The ballot for the approval of the Code has been issued for committee review. A meeting of the Technical Committee (TC) will take place in February 2015 if needed for the disposition of ballot comments. Publication in both English and French is scheduled for August 2015. The next Technical Committee meeting is planned for the week of June 8, 2015, in Niagara Falls, ON.
2015 B149.2 – Propane Storage & Handling Code
The committee last met on June 11, 2014. Public Review took place from March 12 to May 12, 2014, and all comments were dispositioned and resolved. There was a general consensus on the draft and it proceeded to the editing stage. The ballot for the approval of the Code has been issued for committee review. A meeting will take place in February 2015 if needed, for the disposition of ballot comments. Publication in both English and French is scheduled for August 2015. The next Technical Committee meeting is planned for the week of June 8, 2015, in Niagara Falls, ON.
2015 B139 – Installation Code for Oil Burning Equipment
The Technical Committee last met on June 24-26, 2014 to disposition Public Review comments and finalize the technical content in the Draft. The ballot for the approval of the Code took place from Sept. 3 to Oct. 3, 2014. The scope has been changed to include fuel oil storage tanks of all sizes including underground tanks. The Code is now divided into two major parts, B139.1 – Large Installations and B139.2 – Residential and Small Commercial Installations. Publication is scheduled for April 1, 2015, in both English and French.
Gas Appliances and Related Accessories
The CSA Gas Technical Committee held a joint meeting with the U.S. Z21/83 Technical Committee on Sept. 30. 2014. The following new standards were approved:
- CSA 3.8, Gas-fired Equipment for Drying Crops;
- Z21.10.1/CSA 4.1, Water Heaters Volume 1; Z21.10.3/CSA 4.3, Water Heaters Volume Ill;
- Z21.54/CSA 8.4, Gas Hose
- Connectors;
- Z21.19/CSA 1.4, Refrigerators Using Gas Fuel;
- Z21.56/CSA 4.7, Pool Heaters; and
- Z21.58/CSA 1.6, Outdoor Cooking Appliances.
Oil Burning Appliance Standards (B140 Series, B211 & B212)
The B 140 series of Standards have been reaffirmed; however, they are in need of review and updating. The last Technical Committee meeting was held on May 2, 2012. CSA will be looking at reconstituting the TC to begin work on these documents.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors Standard
The Technical Committee has been reinstituted for a new edition of the CSA 6.19 standard. The TC’s first meeting was Sept. 25, 2014, with the publication date projected for September 2016.
Introduction of the Fuels Learning Centre
Recent events provided a business opportunity for me to partner with Bill Egbert in the creation of a new training provider for the fuels industry. The company is called Fuels Learning Center Limited (FLC) which will not only provide training modules to the propane industry but also the fuel oil and natural gas industries.

As most of you are aware Bill was for many years, the General Manager of the Propane Training Institute. I was under contract to the Canadian Propane Association to write new training programs and update existing programs with the latest technical and regulatory requirements.
The Fuels Learning Centre currently has nine provincially approved training courses which reference the latest regulatory requirements of the Codes and the Standards to be adopted:
These programs, when successfully completed, will provide the provincially acceptable ROT and where required the TDG qualifications for persons who need to be trained in the handling and use of propane. We have been able to streamline these programs to focus more on what a person needs to know and less of what is not required to know to safely perform their tasks.
View PDF
 On July 14, 2017, Technical Inspection Services of New Brunswick issued a notice to Gas Industry Stakeholders adopting the most recent versions of CSA codes and standards within their Propane, Natural and Medical Gas Regulations. This includes the 2015 versions of the B149 series and the 2014 edition of the B51 Boiler, pressure vessel, and pressure piping code.
On July 14, 2017, Technical Inspection Services of New Brunswick issued a notice to Gas Industry Stakeholders adopting the most recent versions of CSA codes and standards within their Propane, Natural and Medical Gas Regulations. This includes the 2015 versions of the B149 series and the 2014 edition of the B51 Boiler, pressure vessel, and pressure piping code.